Key Roles of Trace Oxygen Treatment for High‐Performance Zn‐Doped CuI p‐Channel Transistors Transistors and Organic Thin Film Displays
- 저자
- Ao Liu, Huihui Zhu, Kyu In Shim, Jisu Hong, Haksoon Jung, Jeong Woo Han*, and Yong‐Young Noh*
- 저널명
- Advanced Electronic Materials, 7, 1, 2000933 (2021)
- 년도
- 2021
- Link
- https://doi.org/10.1002/aelm.202000933 1047회 연결
[Abstract]
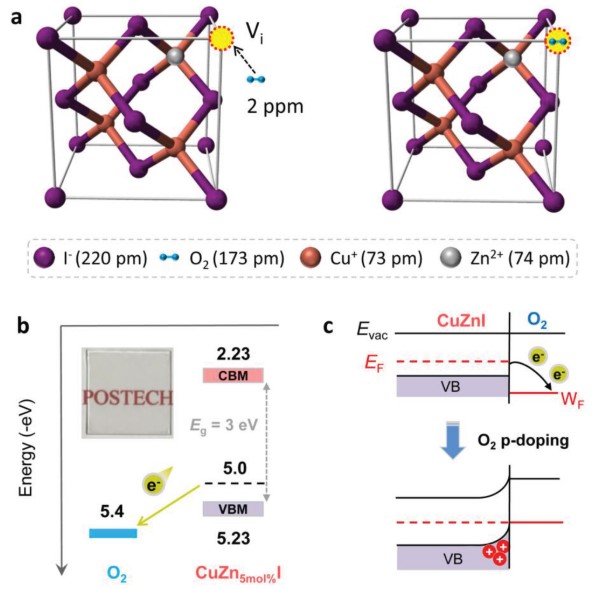
The development of transparent and high-performance p-type semiconductors as a counterpart of n-type metal oxide semiconductors has attracted significant interest for the integration of complementary circuits and p–n junction devices. This study investigates the effect of trace O2 for high-performance and solution-processed inorganic p-channel Zn-doped copper iodide (CuI) thin-film transistors (TFTs) via a combined computation–experiment approach. The absorbed O2 molecules in the CuI film can occupy iodine vacancies, acting as trap passivator. Meanwhile, the strong electronegativity of O2 enables electron capture from the CuI matrix, leading to p-doping. Trace O2-treated Zn-doped CuI TFTs exhibit significantly improved electrical performance compared to untreated devices. Optimized TFTs exhibit a high field-effect hole mobility of 4.4 cm2 V−1 s−1, high on/off current ratio of ≈107, and small hysteresis. These findings provide a clear basis for realizing reproducible and high-performance metal-halide (e.g., CuI and perovskite) optoelectronic devices using low-cost solution process.