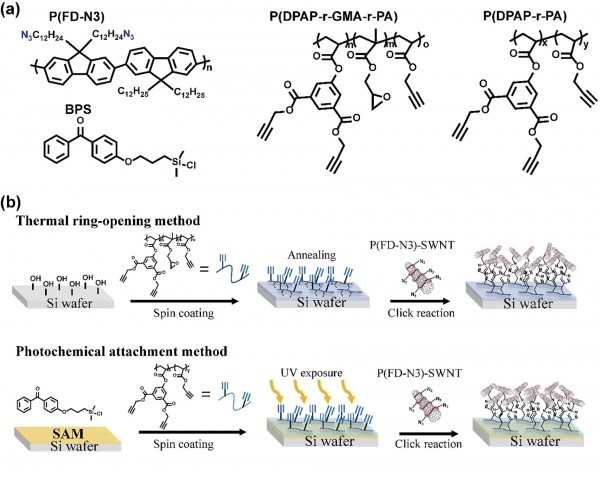
Tailoring the density of carbon nanotube networks through chemical self-assembly by click reaction for reliable transistors
- 저자
- Dongseob Ji, Su Yeol Yoon, Gayoung Kim, Youjin Reo, Seung-Hoon Lee, Henok Getachew Girma, Seungju Jeon, Seo-Hyun Jung, Do-Hoon Hwang, Jin Young Kim, Bogyu Lim*, Yong-Young Noh*
- 저널명
- Chemical Engineering Journal, 452, 3, 139500 (2023)
- 년도
- 2023
- Link
- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.139500 620회 연결