Optical and thermal properties of large-area OLED lightings with metallic grids
- 저자
- Jongwoon Park*, Jongho Lee, Yong-Young Noh
- 저널명
- Organic Electronics, 13, 1, 184-194 (2012)
- 년도
- 2012
- Link
- http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2011.10.024 813회 연결
[Abstract]
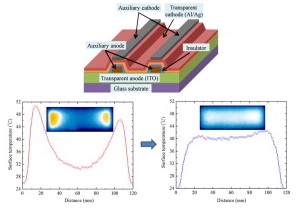
We investigate the effects of auxiliary metal electrodes on the optical and thermal properties of large-area (30 × 120 mm2) opaque and transparent white OLED lighting panels. Enlarging their emission area inevitably entails a non-uniform current distribution due to the limiting conductivity of transparent electrodes, causing local heat generation. To tackle it, we have used grid patterned Cr, Mo/Al/Mo, or Cu metal lines (0.15 mm in width) as auxiliary metal electrodes on an ITO anode. Among those, Cu metal grids exhibit the highest luminous efficacy with the least heat generation, and the most uniform light distribution by virtue of its lowest sheet resistance, followed by Mo/Al/Mo and then Cr metal grids. It is also found that local heat generation appears more seriously in large-area transparent OLED panels. With attempt to suppress it, we have also deposited Al metal lines (2 mm in width) on a semitransparent Al/Ag cathode by thermal evaporation, which brings in a highly uniform heat distribution. Furthermore, we study the effect of the shape of the light-emitting area on the luminance and heat distributions. A round-shaped OLED panel with a hexagonal metal grid exhibits highly homogeneous luminance and surface temperature distributions.