Controlling organization of conjugated polymer films from binary solvent mixtures for high performance organic field-effect transistors
- 저자
- Henry Opoku, Benjamin Nketia-Yawson, Eun Sol Shin, Yong-Young Noh*
- 저널명
- Organic Electronics
- 년도
- 2015
- Link
- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2016.11.004 390회 연결
[Abstract]
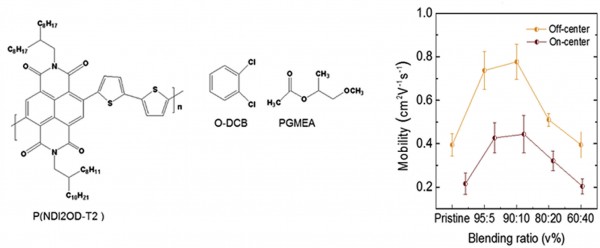
We investigate the effect of a binary solvent blend as a solvent for poly{[N,N′-bis(2-octyldodecyl)-1,4,5,8-naphthalenediimide-2,6-diyl]-alt-5,5′-(2,2′-bithiophene)} P(NDI2OD-T2) on the characteristics of n-channel organic field-effect transistors (OFETs). To make the binary solvent blend, the low-boiling-point non-solvent propylene glycol methyl ether acetate (PGMEA, b.p ∼146 °C) is added to the high-boiling-point good solvent 1,2-dichlorobenzene (O-DCB, b.p ∼180 °C) at various mixing ratio from 0 to 40 v%. UV–vis spectra of P(NDI2OD-T2) solution dissolved in the binary solvent clearly show the formation of polymer aggregates through a gradual red shift of the intramolecular charge transfer band with the addition of high concentrations of non-solvent PGMEA. Higher edge-on oriented crystallinity is observed for P(NDI2OD-T2) films spin-coated from the binary solvent with 5–10 v% PGMEA by out-of-order x-ray diffraction. P(NDI2OD-T2) films are applied as the active layer in top-gate/bottom-contact OFETs. Improved n-type field-effect mobility of the P(NDI2OD-T2) semiconducting layer up to 0.59 cm2/Vs was achieved for on-center spin coated films compared to 1.03 cm2/Vs for off-center (parallel alignment) spin-coated films respectively employing the binary solvent with 10 v% PGMEA.