Systematic Study of Widely Applicable N‐Doping Strategy for High‐Performance Solution‐Processed Field‐Effect Transistors
- 저자
- Jihong Kim, Dongyoon Khim, Kang‐Jun Baeg, Won‐Tae Park, Seung‐Hoon Lee, Minji Kang, Yong‐Young Noh, Dong‐Yu Kim*
- 저널명
- Advanced Functional Materials, 26, 43, 7886-7894 (2016)
- 년도
- 2016
- Link
- https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201602610 491회 연결
[Abstract]
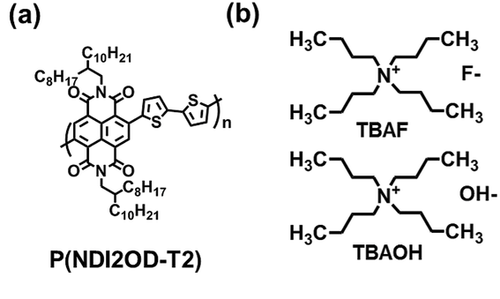
A specific design for solution-processed doping of active semiconducting materials would be a powerful strategy in order to improve device performance in flexible and/or printed electronics. Tetrabutylammonium fluoride and tetrabutylammonium hydroxide contain Lewis base anions, F− and OH−, respectively, which are considered as organic dopants for efficient and cost-effective n-doping processes both in n-type organic and nanocarbon-based semiconductors, such as poly[[N,N′-bis(2-octyldodecyl)-naphthalene-1,4,5,8-bis(dicarboximide)-2,6-diyl]-alt-5,5′-(2,2′-bithiophene)] (P(NDI2OD-T2)) and selectively dispersed semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes by π-conjugated polymers. The dramatic enhancement of electron transport properties in field-effect transistors is confirmed by the effective electron transfer from the dopants to the semiconductors as well as controllable onset and threshold voltages, convertible charge-transport polarity, and simultaneously showing excellent device stabilities under ambient air and bias stress conditions. This simple solution-processed chemical doping approach could facilitate the understanding of both intrinsic and extrinsic charge transport characteristics in organic semiconductors and nanocarbon-based materials, and is thus widely applicable for developing high-performance organic and printed electronics and optoelectronics devices.