Novel Solid-State Solar Cell Based on Hole-Conducting MOF-Sensitizer Demonstrating Power Conversion Efficiency of 2.1%
- 저자
- Do Young Ahn, Deok Yeon Lee, Chan Yong Shin, Hoa Thi Bui, Nabeen K Shrestha*, Lars Giebeler*, Yong-Young Noh, Sung-Hwan Han
- 저널명
- ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9, 15, 12930–12935 (2017)
- 년도
- 2017
- Link
- https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b03487 434회 연결
[Abstract]
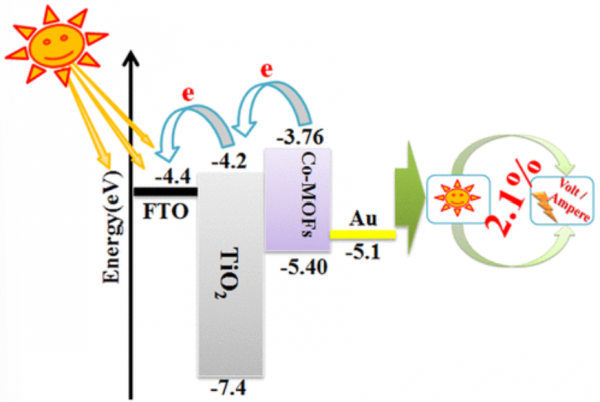
This work reports on designing of first successful MOF-sensitizer based solid-state photovoltaic device, perticularly with a meaningful output power conversion efficiency. In this study, an intrinsically conductive cobalt-based MOFs (Co-DAPV) formed by the coordination between Co (II) ions and a redox active di(3-diaminopropyl)-viologen (i.e., DAPV) ligand is investigated as sensitizer. Hall-effect measurement shows p-type conductivity of the Co-DAPV film with hole mobility of 0.017 cm2 V–1 s–1, suggesting its potential application as hole transporting sensitizer. Further, the energy levels of the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) of Co-DAPV are well-matched to be suitably employed for sensitizing TiO2. Thus, by layer-by-layer deposition of hole conducting MOF-sensitizer onto mesoporous TiO2 film, a power conversion efficiency of as high as 2.1% is achieved, which exceeds the highest efficiency values of MOF-sensitized liquid-junction solar cells reported so far.