Effect of vacuum metalized gate electrode in top-gate solid-state electrolyte-gated organic transistors
- 저자
- Benjamin Nketia-Yawson, Grace Dansoa Tabi, Yong Xu, Yong-Young Noh*
- 저널명
- Organic Electronics, 55, 63-68 (2018)
- 년도
- 2018
- Link
- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2018.01.011 471회 연결
[Abstract]
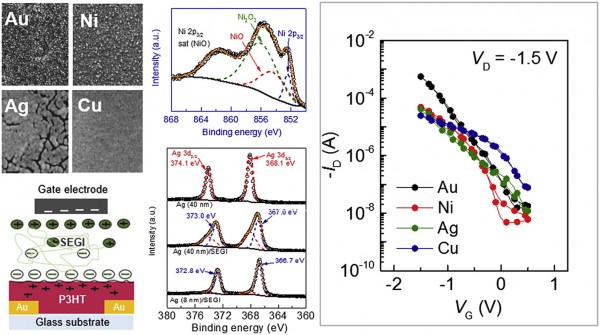
We report the effect of the metal-gate electrode in top-gate solid-state electrolyte-gated transistors (SEGTs). Here, a P(VDF-TrFE):P(VDF-HFP)-[EMIM][TFSI] dielectric blend is used as the solid-state electrolyte gate insulator (SEGI), with a variety of metal-gate electrodes, such as gold (Au), nickel (Ni), silver (Ag), and copper (Cu), and poly(3-hexylthiophene-2,5-diyl) (P3HT) as a semiconductor. Among the employed metal-gate electrodes, we achieved highest hole mobility of 3.26 ± 0.67 cm2V−1s−1 in Au-gated P3HT SEGTs, which is ten times greater than the other metal-gated devices. The remarkable mobility in Au-gated devices is attributed to low contact resistance (Rc < 2 kΩ cm) and the exceptional electrochemical stability of the gold electrode. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis reveals the formation of the oxide layers (NiO, Ni2O3, Cu2O, AgxO) at the thermally-evaporated thin metal/SEGI interface. In a metal-insulator-semiconductor capacitor, the highly-conductive Ag and Cu based capacitors measured higher specific capacitance above 30 μFcm−2 compared to Au and Ni capacitors (∼10 μFcm−2) based on the same SEGI composition. Our findings provide useful insight for enhancing the charge injection and transport properties in top-gated electrolyte-gated transistors by selecting the appropriate top-gate metal electrode.